GK Physiotherapy Centre has been providing comprehensive services in the treatment, prevention and consultation of the following:.
Shoulder Conditions:
1) Frozen shoulder(stiff shoulder) 2) Rotater cuff lesions 3) Dislocations or recurrence of shoulder joint 4) Shoulder Tendinitis & Impingement syndromes 5) Acromioclavicular joint injuries(A-C joint) 6) Labral Tears . Patient Symptoms : Patients come up with pain, restricted shoulder movements, muscle weakeness or weakness in gripping or reduced muscle seize or muscle atropy in the shoulder region . Treatment Procedure : First step would be to make a detailed physiotherapy assessment after the diagnosis is done aims are set for the treatment plan . - Reduce pain &inflammation : Suitable electrotherapy modalities are selected to reduce pain inflammation . - Reduction of joint stiffness : Here specialized mobilization or joint movement is done by physiotherapist known as passive shoulder mobilization with glides and with active exercises by patient . - Cervical postural Strengthening : Muscle strengthening is done using weights or terrabands depending on other criteria of patients. . - Patients are taught with certain home care exercises to continue with and are asked to come back for the review. - Muscle spasms.
Frozen shoulder(stiff shoulder): Treatment
Frozen shoulder(stiff shoulder) Adhesive Capsulitis, or a frozen shoulder, is a poorly understood condition in which the deepest layers of soft tissue, called the joint capsule, become diseased. Shoulder range of motion becomes very limited and painful. The cause of a frozen shoulder is still not known but minor traumas, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, psychiatric patients, post-surgical patients, and prolonged immobilization of the shoulder may in someway cause this condition. The disease is characterized as having freezing, frozen, and thawing stages, and is self-limiting (in time it goes away on its own). However, it can take two years or more to recover from this condition.
Rotater cuff lesions:
Treatment
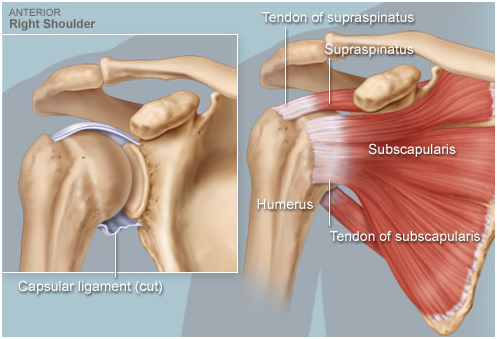 Rotator cuff tears happen in younger people when they experience a trauma such as a fall. In middle-aged people and seniors, rotator cuff tears are usually the result of a gradual wearing out of the rotator cuff tendon(s). The signs and symptoms of rotator cuff tears are pain in the shoulder often radiating down to the middle of the arm especially when the arm is raised overhead, weakness, and in severe cases, a complete loss of the ability to lift the arm. Treatment in young and middle-aged patients is usually arthroscopic or open repair of the torn tendons. In older patients, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy and cortisone injections.
Rotator cuff tears happen in younger people when they experience a trauma such as a fall. In middle-aged people and seniors, rotator cuff tears are usually the result of a gradual wearing out of the rotator cuff tendon(s). The signs and symptoms of rotator cuff tears are pain in the shoulder often radiating down to the middle of the arm especially when the arm is raised overhead, weakness, and in severe cases, a complete loss of the ability to lift the arm. Treatment in young and middle-aged patients is usually arthroscopic or open repair of the torn tendons. In older patients, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy and cortisone injections.
Dislocations or recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint Shoulder : Treatment
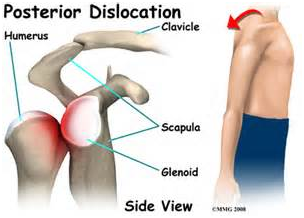
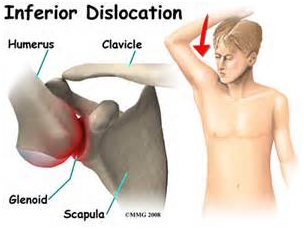 Shoulder instability occurs when the shoulder moves completely out of its socket (dislocation) and requires a medical professional to relocate it, or to a lesser degree, when it slips out of joint but spontaneously move back in place (subluxation). Usually, the shoulder dislocates or subluxes forward (this is called an anterior dislocation). Much less often, it dislocates backward (posterior dislocation), and sometimes, it can slip out forward, backward, or downward (this is called multidirectional instability). The shoulder is most at risk for anterior dislocation when the arm is placed in an abducted and external rotated position (such as a fall on the outstretched hand or tackling a player).
An anterior dislocation is obvious because it is immediately noticed by the person right after the trauma. However, minor instability may result in a sensation that the shoulder is slipping out of place with or without pain. One might also experience pain or a sense of apprehension when the arm is abducted and externally rotated (ask your physical therapist about this).
A sudden dislocation is an emergency. The patient should be taken to the emergency room immediately to make sure there is no damage to the blood vessels or nerve that go to the shoulder, arm, and hand. Usually, the emergency room physician can move the arm in such a way that the dislocated shoulder reduces back into its proper place. Rarely is surgery indicated. Pain and muscle relaxant medication is often prescribed. Ice can also help reduce the pain. Physical therapy is usually started 2-3 weeks after a dislocation to strengthen the muscles that support the shoulder joint.
Shoulder instability occurs when the shoulder moves completely out of its socket (dislocation) and requires a medical professional to relocate it, or to a lesser degree, when it slips out of joint but spontaneously move back in place (subluxation). Usually, the shoulder dislocates or subluxes forward (this is called an anterior dislocation). Much less often, it dislocates backward (posterior dislocation), and sometimes, it can slip out forward, backward, or downward (this is called multidirectional instability). The shoulder is most at risk for anterior dislocation when the arm is placed in an abducted and external rotated position (such as a fall on the outstretched hand or tackling a player).
An anterior dislocation is obvious because it is immediately noticed by the person right after the trauma. However, minor instability may result in a sensation that the shoulder is slipping out of place with or without pain. One might also experience pain or a sense of apprehension when the arm is abducted and externally rotated (ask your physical therapist about this).
A sudden dislocation is an emergency. The patient should be taken to the emergency room immediately to make sure there is no damage to the blood vessels or nerve that go to the shoulder, arm, and hand. Usually, the emergency room physician can move the arm in such a way that the dislocated shoulder reduces back into its proper place. Rarely is surgery indicated. Pain and muscle relaxant medication is often prescribed. Ice can also help reduce the pain. Physical therapy is usually started 2-3 weeks after a dislocation to strengthen the muscles that support the shoulder joint.
Shoulder Tendinitis & Impingement syndromes: Treatment
Tendinitis is an inflammation of the shoulder tendons. The signs of inflammation are pain, warmth, redness, tenderness to touch, and loss of function. Shoulder tendinitis (often called Rotator Cuff Tendonitis) can occur when the rotator cuff is overloaded, fatigued, traumatized, and with age-related degenerative changes. Pinching or impingement of the rotator cuff tendons occurs in a region under a bony structure called the acromion (the projection of the shoulder blade that forms the tip of the shoulder). Impingement happens when the arm is raised overhead repeatedly, or raised overhead with a heavy load in your hand, or may occur when you sleep on your shoulder.
Treatment for impingement or rotator cuff tendonitis usually involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications ,physical therapy to restore proper strength and movement, and less often, a cortisone injection.
Labral Tears: Treatment
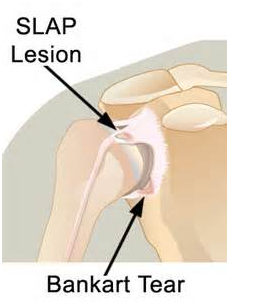
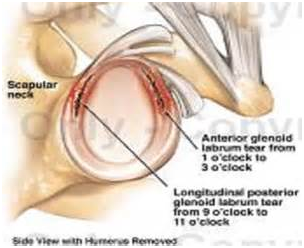 The labrum is a cartilage ring that surrounds the shoulder socket (called the glenoid) and makes it deeper. Labrum or labral tears are usually associated with trauma, instability of the shoulder, or repetitive throwing as with a baseball player.
The signs and symptoms of a labral tear are painful clicking, locking, or popping. Instability may be present because the labrum is not doing its job of holding the ball in the socket. Medical intervention for a labral tear typically involves an MRI for diagnosis and arthroscopic repair but labral tears are often hard to diagnose. A special kind of labral tear, a superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear, often involves the biceps tendon as well.
The labrum is a cartilage ring that surrounds the shoulder socket (called the glenoid) and makes it deeper. Labrum or labral tears are usually associated with trauma, instability of the shoulder, or repetitive throwing as with a baseball player.
The signs and symptoms of a labral tear are painful clicking, locking, or popping. Instability may be present because the labrum is not doing its job of holding the ball in the socket. Medical intervention for a labral tear typically involves an MRI for diagnosis and arthroscopic repair but labral tears are often hard to diagnose. A special kind of labral tear, a superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear, often involves the biceps tendon as well.
Acromioclavicular joint injuries(A-C joint): Treatment
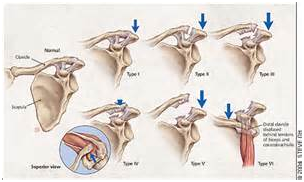 A-C joint injuries is commonly the result of a fall on the end of the shoulder. It results in pain, swelling, and often deformity in which it appears that the collar bone is sticking up.
Treatment for a acromioclavicular joint injuries are usually involves rest, ice, pain and anti-inflammatory medication, and physical therapy to restore motion. Rarely is surgery indicated. However, sometimes the ligaments that attach the collar bone to the shoulder blade are repaired.
A-C joint injuries is commonly the result of a fall on the end of the shoulder. It results in pain, swelling, and often deformity in which it appears that the collar bone is sticking up.
Treatment for a acromioclavicular joint injuries are usually involves rest, ice, pain and anti-inflammatory medication, and physical therapy to restore motion. Rarely is surgery indicated. However, sometimes the ligaments that attach the collar bone to the shoulder blade are repaired.
Copyright © 2013 GK Physiotherapy Clinic | Bangalore
