GK Physiotherapy Centre has been providing comprehensive services in the treatment, prevention and consultation of the following:.
Knee Joint Conditions:
1)Meniscal Tears 2) Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear 3)Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear 4) Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tear 5) Patello-femoral Pain 6) Knee Osteoarthritis .
Meniscal Tears : Treatment
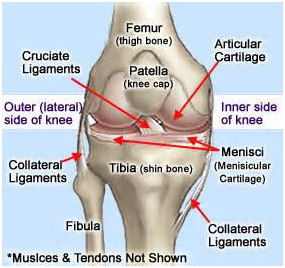
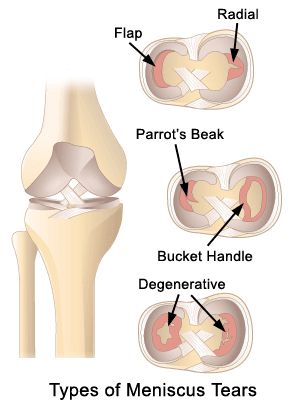 The menisci (plural for meniscus) are cartilage pads, which function to cushion the compressive loads in the knee. One or both of these pads can be torn which often occurs when the lower leg is forcefully bent and twisted. Signs and symptoms include joint line pain, locking and swelling of the knee. The tear often has a bucket handle or parrot beak shape. Treatment should consist of rest, ice, compression and elevation. Arthroscopic surgery is indicated for a large tear.This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
The menisci (plural for meniscus) are cartilage pads, which function to cushion the compressive loads in the knee. One or both of these pads can be torn which often occurs when the lower leg is forcefully bent and twisted. Signs and symptoms include joint line pain, locking and swelling of the knee. The tear often has a bucket handle or parrot beak shape. Treatment should consist of rest, ice, compression and elevation. Arthroscopic surgery is indicated for a large tear.This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear :
Treatment
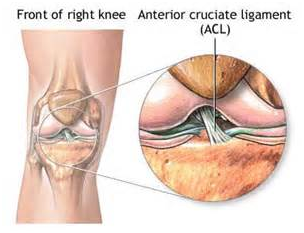
 The cruciate (or crossing) ligament stabilizes the knee. The anterior cruciate (ACL) may completely break (rupture) when the knee is bent beyond its normal range of motion or with excessive twisting. Signs and symptoms include a ‘pop’ sensation with significant swelling and pain. There is a sense of instability or the knee giving away. Initial treatment includes rest, ice, elevation, and compression. Physical therapy consisting of progressive strengthening and functional exercise may facilitate recovery. If knee instability persists, surgery is indicated. The middle third of the patellar tendon, hamstrings, or cadaver ligament may be used to reconstruct the lost ligament.
This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
The cruciate (or crossing) ligament stabilizes the knee. The anterior cruciate (ACL) may completely break (rupture) when the knee is bent beyond its normal range of motion or with excessive twisting. Signs and symptoms include a ‘pop’ sensation with significant swelling and pain. There is a sense of instability or the knee giving away. Initial treatment includes rest, ice, elevation, and compression. Physical therapy consisting of progressive strengthening and functional exercise may facilitate recovery. If knee instability persists, surgery is indicated. The middle third of the patellar tendon, hamstrings, or cadaver ligament may be used to reconstruct the lost ligament.
This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear : Treatment
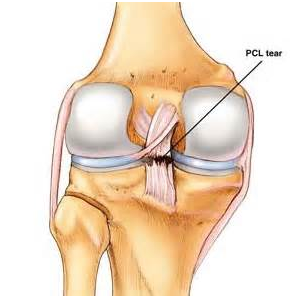
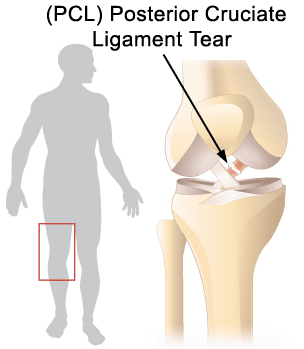 The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is stronger and less commonly injured. Motor vehicle accident, when the knee(s) forcefully impact the car dashboard, is a common mechanism of injury. Initial treatment includes rest, ice, elevation, and compression. Physical therapy consisting of progressive strengthening and functional exercise may facilitate recovery. Surgery is not typically required.
This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position..
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is stronger and less commonly injured. Motor vehicle accident, when the knee(s) forcefully impact the car dashboard, is a common mechanism of injury. Initial treatment includes rest, ice, elevation, and compression. Physical therapy consisting of progressive strengthening and functional exercise may facilitate recovery. Surgery is not typically required.
This injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position..
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tear : Treatment
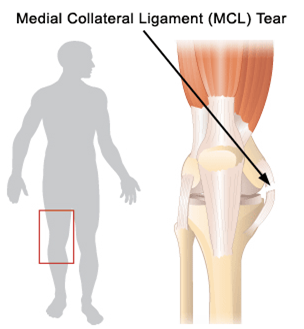 MCL tears are common injuries. A forceful stress on the outside of the knee can cause a stretching and injury of the MCL. Signs and symptoms include knee pain at the inner aspect and swelling. Medial meniscal tears and ACL injury may occur with severe trauma (commonly occurs during football and soccer). Initially, rest, ice, elevation and compression is necessary followed by bracing and rehabilitation. Severe tears may require surgeryThis injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position
MCL tears are common injuries. A forceful stress on the outside of the knee can cause a stretching and injury of the MCL. Signs and symptoms include knee pain at the inner aspect and swelling. Medial meniscal tears and ACL injury may occur with severe trauma (commonly occurs during football and soccer). Initially, rest, ice, elevation and compression is necessary followed by bracing and rehabilitation. Severe tears may require surgeryThis injury is commonly the result of quick sprints or quick stops while running. With a muscle strain, there is localized tenderness or a bulge in the tender area of the thigh. The pain is aggravated by lifting the thigh (a straight leg raise), ascending/descending stairs, or getting up from a seated position
Patello-femoral Pain (Commonly Called Chondromalacia Patella) : Treatment
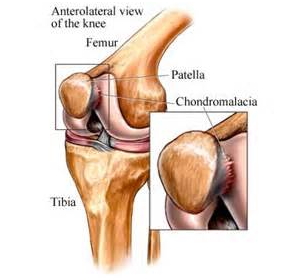 Chondromalacia meaning softening of the patellar cartilage, is a common misdiagnosis. Softening of the cartilage can only be detected by directly visualizing the cartilage during surgery. The correct diagnosis for pain and swelling originating from under the kneecap is Patello-femoral Pain.
Treatment includes pain relief with rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Swelling must be controlled. Anti-inflammatory medications, bracing, and physical therapy are often helpful. Progressive strengthening of the quadriceps is essential. Occasionally, foot orthoses may be helpful. Rarely, surgery is required to assist in realigning the kneecap by releasing the tight structures on the outside of the kneecap and reefing the inner structures
Chondromalacia meaning softening of the patellar cartilage, is a common misdiagnosis. Softening of the cartilage can only be detected by directly visualizing the cartilage during surgery. The correct diagnosis for pain and swelling originating from under the kneecap is Patello-femoral Pain.
Treatment includes pain relief with rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Swelling must be controlled. Anti-inflammatory medications, bracing, and physical therapy are often helpful. Progressive strengthening of the quadriceps is essential. Occasionally, foot orthoses may be helpful. Rarely, surgery is required to assist in realigning the kneecap by releasing the tight structures on the outside of the kneecap and reefing the inner structures
Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper´s Knee) : Treatment
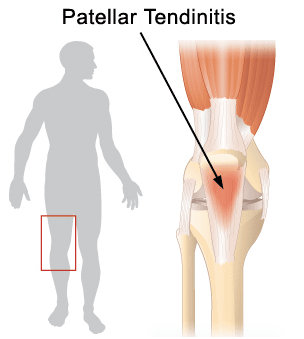 Jumping sports (such as basketball and volleyball) put a huge load on the kneecap and attached tendons. Signs and symptoms of patellar tendonitis include pain to touch directly on the patellar tendon and occasionally, swelling. Treatment includes activity modification, and physical therapy.
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson is a specific disorder of the patellar tendon where it attaches to the base of the kneecap. In contrast, Osgood-Schlatter disease is a disorder of the tendon where it attaches at the tibial tuberosity of the leg. Both are common disorders in maturing teens.
Jumping sports (such as basketball and volleyball) put a huge load on the kneecap and attached tendons. Signs and symptoms of patellar tendonitis include pain to touch directly on the patellar tendon and occasionally, swelling. Treatment includes activity modification, and physical therapy.
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson is a specific disorder of the patellar tendon where it attaches to the base of the kneecap. In contrast, Osgood-Schlatter disease is a disorder of the tendon where it attaches at the tibial tuberosity of the leg. Both are common disorders in maturing teens.
Knee Osteoarthritis : Treatment
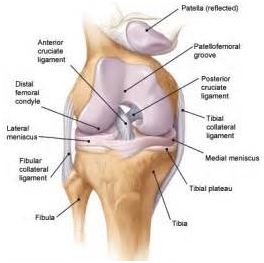
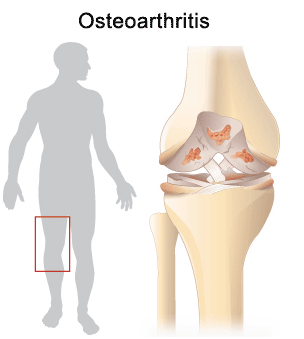 Osteoarthritis of the knee occurs when the cartilage coverings on the end of the femur and the top of the tibia wear out. The tibia has two special cartilage pads called menisci (one is called a meniscus). This cartilage becomes flattened, bone spurs form, the joint becomes inflamed, range of motion is lost, there is ensuing weakness, pain and difficulty with walking, climbing stairs, and getting in/out of chairs. Physical therapy can help with recovery of range of motion, strength, walking skills, and pain management.
Osteoarthritis of the knee occurs when the cartilage coverings on the end of the femur and the top of the tibia wear out. The tibia has two special cartilage pads called menisci (one is called a meniscus). This cartilage becomes flattened, bone spurs form, the joint becomes inflamed, range of motion is lost, there is ensuing weakness, pain and difficulty with walking, climbing stairs, and getting in/out of chairs. Physical therapy can help with recovery of range of motion, strength, walking skills, and pain management.
Copyright © 2013 GK Physiotherapy Clinic | Bangalore
